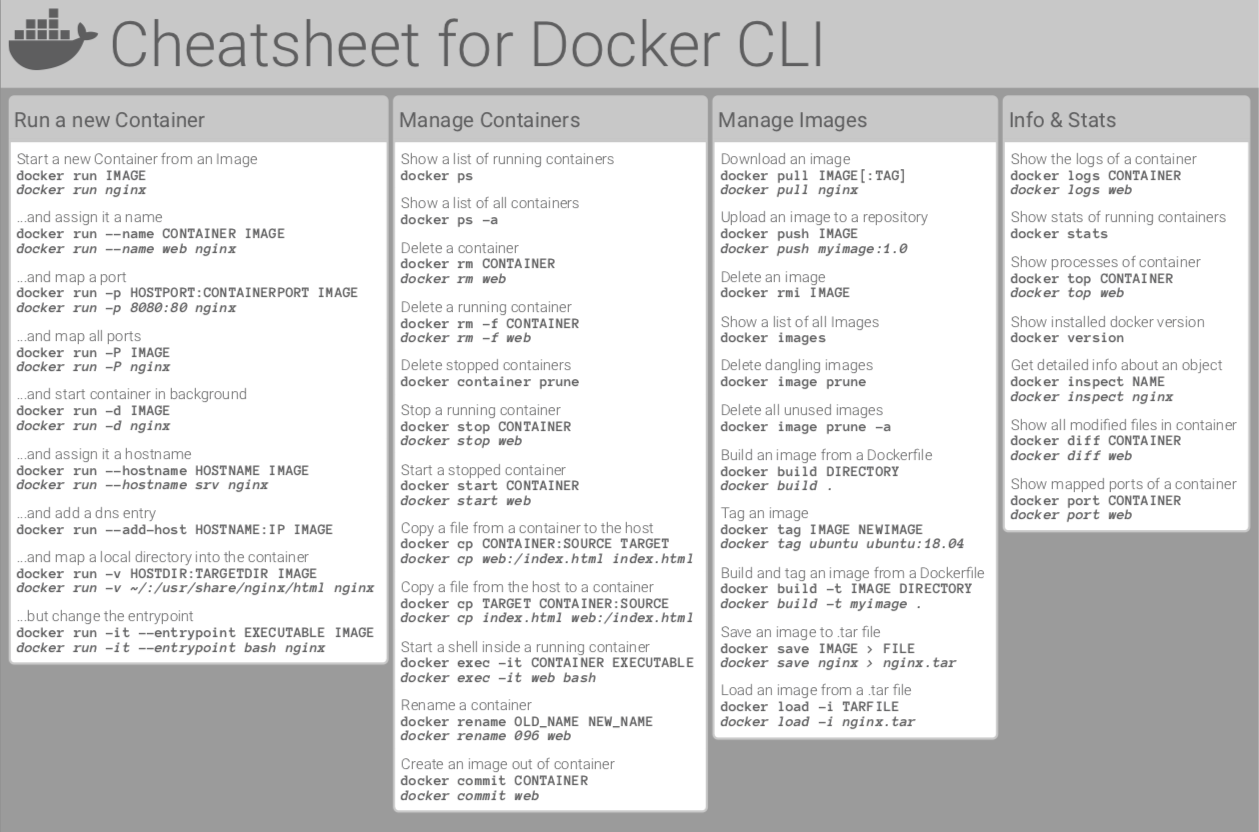
TLDR
start a new container and run it
docker run
resume a container
docker start <container_id>
stop a container
docker stop <container_id>
Find the name or ID of the image/ container
docker [image|container] ls
stop all container
docker container stop $(docker container ls -aq)
remove all stop container/image, -f for removing the running container
docker container|image [-f] prune
delete a image
docker rmi <image>
delete all images
docker image rm $(docker image ls -aq)
Build/Re-buld image from the dockerfiles (customize)
Docker build . -t <custom_container_name> <folder location (eg .)>
Use the docker run command to initiate the container using the image. Automatically pull image if not exist locally
docker run --name some-postgres -e POSTGRES_PASSWORD=mysecretpassword -d -p 5432:5432 postgres:13-alpine
or use -it to open interactive mode to use the bash within containers
Docker run -it < image name> bash
After run, Use the docker exec command to start a shell inside the container. Replace “container_name_or_id” with the name or ID of the container.
docker exec -it <container_name_or_id> <bash>
//e.g. <bash> = /bin/bash
Use docker inspect to check the IP of the container:
docker inspect 2fbd05836471
rename tag
docker tag <old_name> <new_name>
ports:
# default address = 0.0.0.0
docker run -p 50000:5000
# You can also specify the address before the localhost port
docker run -p 127.0.0.1:5000:5000
Combined example
#create a new container from img, in detached mode exposed 3000 port of local host to 80 port in container. Auto-emove the container after stopping it, rename it as <container name>
docker run -p 3000:80 -d --rm --name <container_name> <container_id>