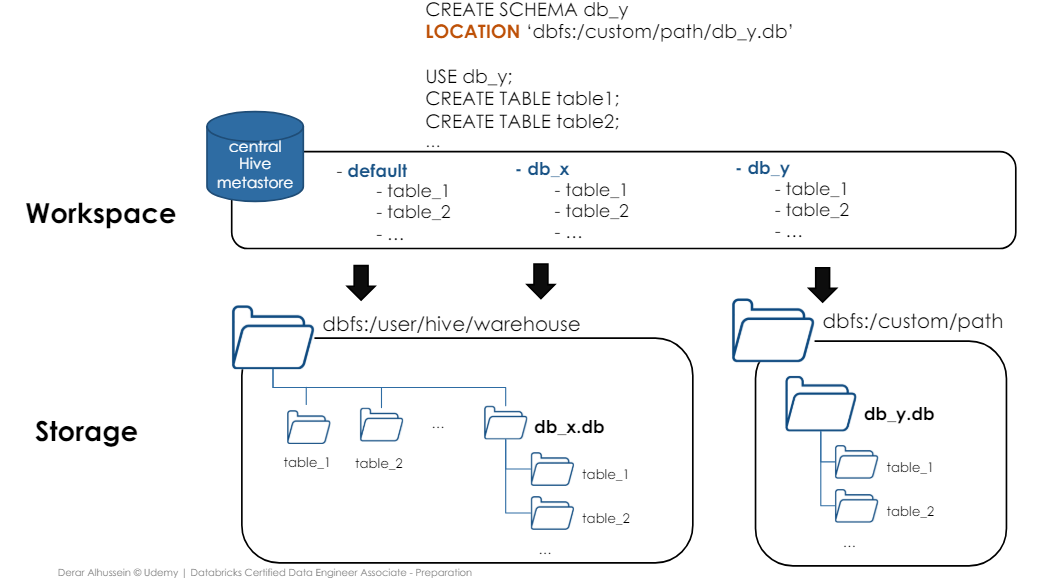
databases = schemas in Hive metasore create database db_name = create schema db_name
HIve Metastore
- Repository of metadata that stores information for data structure (databases, table, partition)
- table definition, format, path to the storage
Default path when create database: dbfs:/user/hive/warehouse
Every workspace has central hive metastore accessible by all cluster to persist table metadata
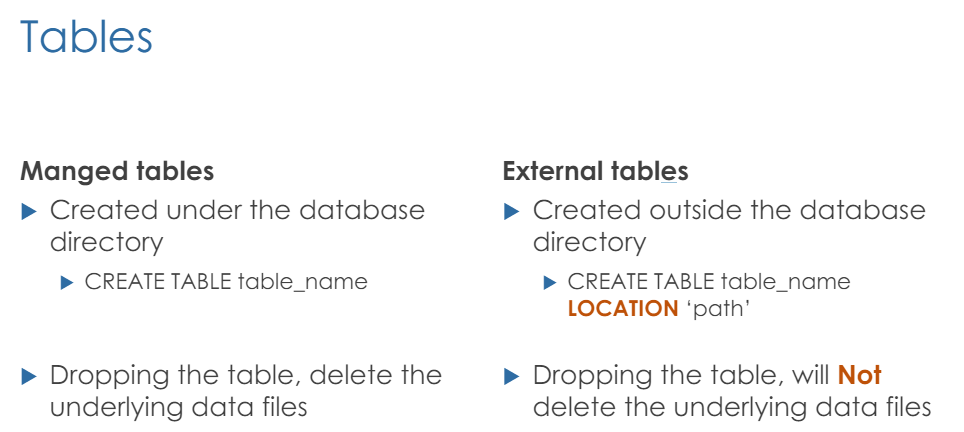
- without specifying, hive metastore is default (managed tables)
- with LOCATION syntax, we can create a storage in custom location other than default dbfs:/user/hive/warehouse (External tables)
Two types of tables
To create external tables outside the default hive warehouse
use db_x; //specify the DB
create table table_name
LCOATION 'dbfs:/some/path/table_name' //specify the storage location
The table is classified as external as long as you use LOCATION syntax, even you specify the location as hive path: dbfs:/user/hive/warehouse/<Table_Name>
CTAS: we can create the table via CTAS with additional options:
CREATE TABLE new_table
COMMENT "<some_comment>"
PARTITIONED BY (col1,col2)
LOCATION '/some/path'
AS SELECT col1, col2, col3 as new_col3, FROM old_table
Noted that CTAS do not support manual schema declaration (e.g. data type), it is automatically inferred
Table Constraints:
- NOT NULL/ CHECK
- ALTER TABLE table name ADD CONSTRAINT constraint name constraint details (e.g. ALTER TABLE orders ADD CONSTRAINT valid_date CHECK (date > ‘2020-01-01)
Cloning Delta lake tables:
- Useful to set up tables for testing in dev
- Two ways, in either case, data modifications will not affect the source
- DEEP CLONE
- Fully copies data + metadata from a source table to a target
- can sync changes
- take quite a while for large dataset
CREATE TABLE table_clone
DEEP CLONE source_table
- SHALLOW CLONE
- just copy the delta transaction logs (no data moving so it’s quick)
CREATE TABLE table_clone
SHALLOW CLONE source_table
View
- logical query against source tables, execute when querying
- 3 Types
- (stored) Views
- persisted objects
CREATE VIEW view_name AS qeury - dopped only by
DROP VEIW
- persisted objects
- Temporary Views
- session-scoped view, a session is created when:
- opening a new notebook
- detaching and reattaching to a cluster
- installing a python package
- restarting a cluster
- `CREATE TEMP VIEW view_name AS qeury
- dropped when session ends
- session-scoped view, a session is created when:
- Global Temporary View
- Cluster-scoped view, as long as cluster is running, any notebook attached to that cluster can access its global temporary across sessions
- `CREATE GLOBAL TEMP VIEW view_name AS qeury
- `SELECT * FROM global_temp.view_name
- dropped when cluster restarted
- (stored) Views
See all tables and views
SHOW TABLES;
SHOW TABLES IN global_temp; //for global view