-
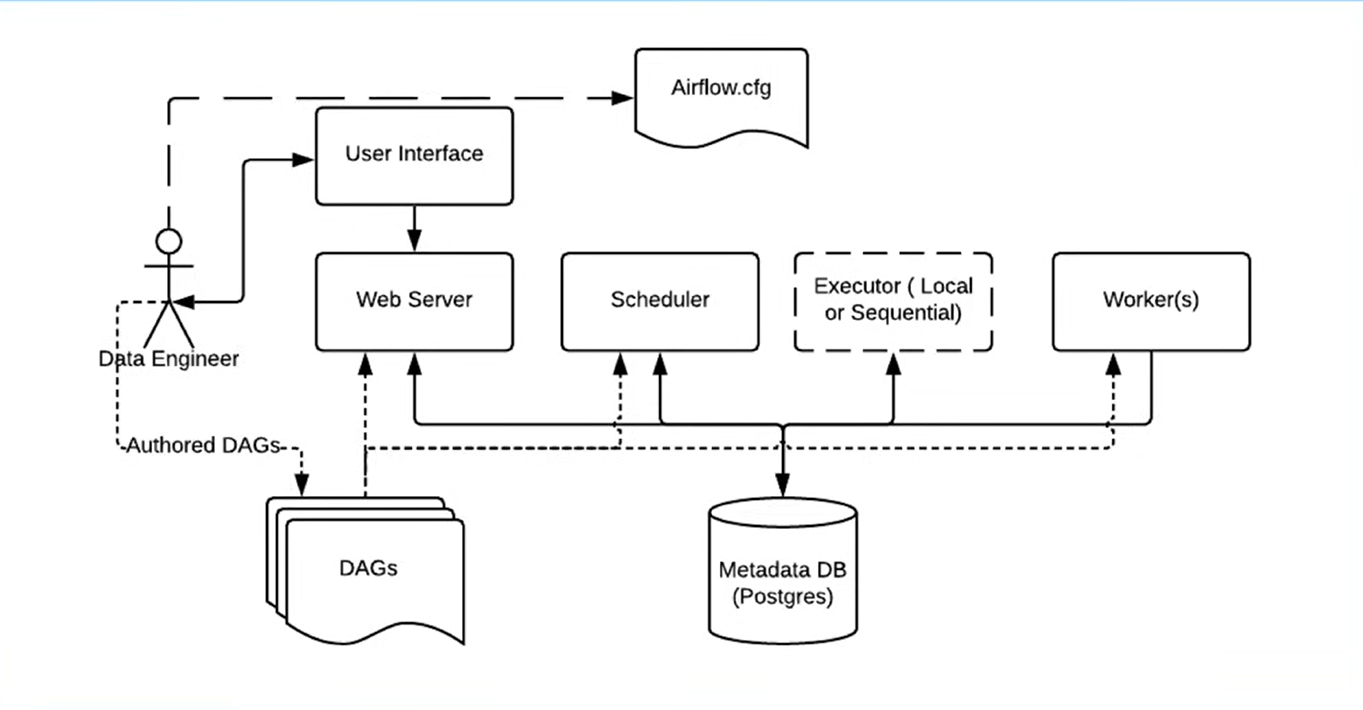
Data engineer created all the pipeline and configure the airflow setup via airflow.cfg, like type of executor and which DB to use.
-
Data Engineers create and manage the DAGs they authored in a UI supported by the web server.
-
The DAGs are visible to scheduler. The scheduler reads from the metadata database to check on the status of each task and decide what needs to get done and when, and change the task’s status thought-out the Task Lifecycle
-
The webserver: provides UI allow user to view, manage, and monitor workflows through web browser
-
The scheduler responsible for determining when tasks should run and ensure they run at the right time and right order
-
Meta Database: Stores information about user, tasks and their status
-
The triggerer: managing deferrable tasks for external events without blocking other processes
-
The executor: like a traffic controller, works closely with the scheduler to determine what resources will actually complete those tasks (using a worker process
-
or otherwise) as they’re queued, and whether to run task in sequence or in parallel. It doesn’t execute task, it determines how to run tasks
-
The Worker: the process that actually perform the task
-
In order to persist the update and retrieve the info of DAGs, webserver, scheduler, executor and worker connected to a DB closely where the metadata were stored